SpaceX launched the world’s most powerful rocket on its fourth flight on Thursday, successfully deploying the company’s Starship upper stage into space and then bringing it back down through re-entry heat for an apparent splash. controlled in the Indian Ocean, despite heavy damage to at least. a steering feather.
The giant Super Heavy first stage booster also made a controlled descent to a “soft” landing in the Gulf of Mexico after extracting the Starship from the lower atmosphere. It was the first time that both stages were able to meet the main objectives of the test flight.
“Despite the loss of many plates (heat shields) and a damaged collision, the Starship made it to a soft landing in the ocean!” SpaceX founder Elon Must said on X. “Congratulations to the @SpaceX team on an epic achievement!”
SpaceX
The 397-foot-long rocket blasted off from SpaceX’s Boca Chica, Texas, Starbase flight facility at 8:50 a.m. EDT, thundering away from the Gulf Coast with the power of 33 methane-burning Raptor engines in the Super First Stage Heavy. .
With Musk watching from the company’s launch control center, holding one of his children on his lap, the Super Heavy-Starship rose from its pad on a brilliant jet of flaming exhaust, arcing eastward as sped towards the sky.
SpaceX
Capable of generating 16 million pounds of thrust during the initial stages of flight, the rocket is by far the most powerful launcher ever built with more than twice the liftoff thrust of the spacecraft, NASA’s legendary Apollo Saturn 5 program, and the rocket Space Launch System. designed for the agency’s Artemis moon rocket.
Despite one Raptor shutting down early, the Super Heavy pulled the Starship upper stage out of the dense lower atmosphere, then separated, turned, and restarted multiple engines to reverse course and head back toward the Gulf Coast . The Starship, meanwhile, powered by its six Raptors, continued its ascent into space itself.
Early on for the test program, the Super Heavy performed a controlled descent, firing three engines to slow for a splash amid waves of wild cheers and applause at the SpaceX factory in Hawthorne, California, as live television images showed the tail of the rise . splash in water.
SpaceX
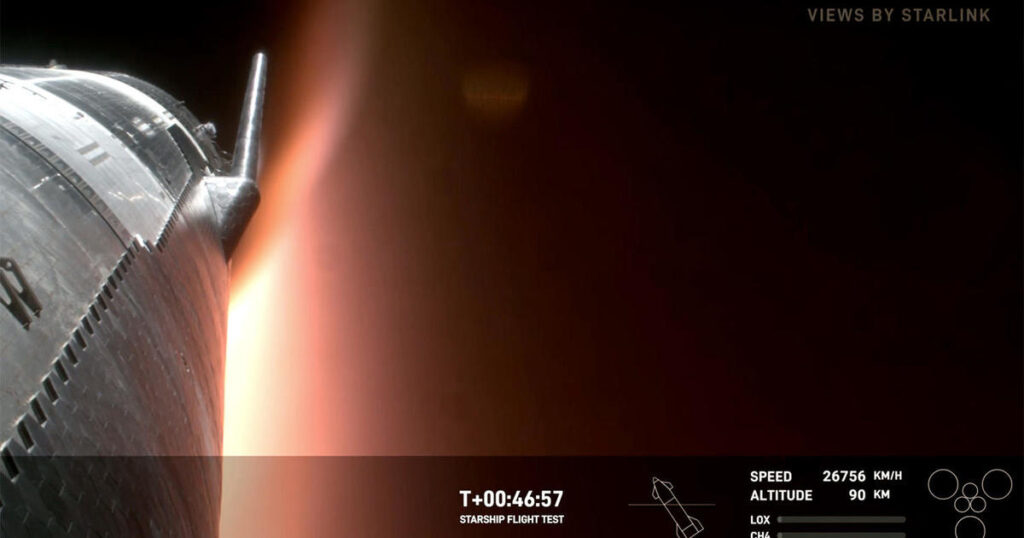
The 160-foot-long Starship, meanwhile, reached its planned sub-orbital trajectory as planned and then headed around the world before falling back into the atmosphere. Live television footage showed the rocket bathed in the red glow of atmospheric friction as it plunged belly-first into the lower atmosphere.
During the rocket’s third test flight in March, Starship did not survive its encounter with atmospheric friction, disintegrating at high altitude. This time, the vehicle appeared stable as it plunged back to Earth, bathed in super-hot plasma that could be seen engulfing the rocket’s belly and guidance fins.
As the descent continued, a camera showed the heat eating away at a steering fin, with chunks of burning debris being ripped off.
“That’s a nail!” exclaimed SpaceX commentator Kate Tice.
SpaceX
Amazingly, data from the Starship continued to flow and the vehicle’s engines were fired again for the planned landing burn. What orientation the ship was in when it hit the water could not be seen in the footage from a visibly damaged camera, but getting to that point marked a major achievement.
“It was unbelievable,” said SpaceX spokesman Dan Huot. “I can’t wait until the next one.”
SpaceX
Both the Super Heavy and Starship boosters are designed to be fully reusable. Once operational, SpaceX plans to fly the first stage back to the launch site, where it will be picked up by giant mechanical arms at its launch port. The Starship is designed to land on any available location, be it on Earth, the Moon or even Mars.
But for the Super Heavy-Starship’s initial test flights, recovery was not an option. The goal was to “simply” return both phases to the lower atmosphere intact and under control.
SpaceX
“The fourth flight test shifts our focus from achieving orbit to demonstrating the ability to return and reuse the Starship and Super Heavy,” SpaceX said on its website. “The primary objectives will be to execute a landing burn and soft splash in the Gulf of Mexico with the Super Heavy booster and achieve a controlled entry of the Starship.”
During three previous flights, two in 2023 and the most recent in March, the Super Heavy and Starship stages suffered catastrophic failures before all test objectives could be met. But with each flight, SpaceX implemented hardware and software improvements that resulted in dramatic performance improvements.
On the third test flight, the Starship upper stage reached space, orbited the planet and began a planned descent over the Indian Ocean before blasting off in the upper atmosphere. The Super Heavy Booster returned to the lower atmosphere over the Gulf of Mexico before losing control.
But SpaceX hailed the flight as an overall success and made more changes to improve performance during Thursday’s test.
The regular flight of the Super Heavy-Starship is essential to it NASA’s Artemis Moon Program. NASA awarded SpaceX a $2.9 billion contract in 2021 to develop a variant of the Starship upper stage to transport astronauts from lunar orbit down to the surface and back. Artemis crews will travel to and from the Moon using Orion capsules built by Lockheed Martin.
SpaceX (edited by CBS News)
To get to the Moon, several Super Heavy tanker flights would need to be launched to robotically resupply an upper Starship already in low Earth orbit. The Starship lander will then fly itself into lunar orbit to receive the Artemis moon walkers.
NASA’s contract requires an unmanned lunar landing test flight before astronauts make an actual landing attempt. Artemis managers are targeting late 2026 for the first lunar landing with astronauts on board.
But that will depend on SpaceX launching enough Super Heavy-Starship flights to demonstrate reliability. While SpaceX’s philosophy is to fly often, learn from mistakes and fly again, NASA will require a long string of successful flights before the agency deems it safe to put astronauts aboard.